
If typical signs and symptoms are not present, laboratory testing can confirm a diagnosis of tickborne disease.

In patients with characteristic symptoms such as EM, laboratory testing is often not required but can be used to confirm a diagnosis. Some tickborne diseases present with telltale symptoms for example, individuals with Lyme disease typically have a characteristic erythema migrans (EM) rash. In general, tickborne disease may be suggested by a combination of clinical presentation and supportive travel history, activity, or geographic area of residence. Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) can be used but is generally insensitive in early disease.
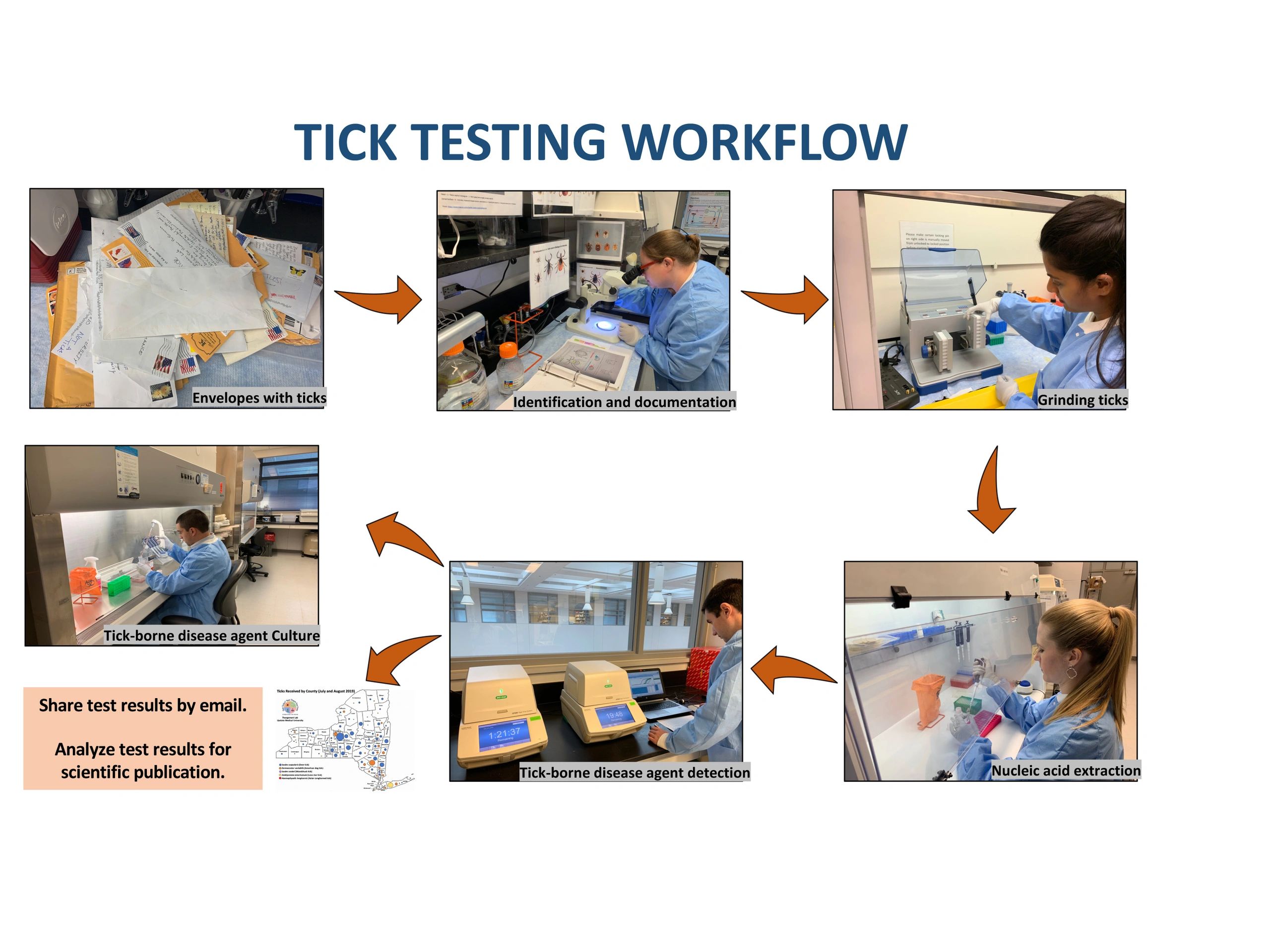
NIETO LAB TICK TESTING SKIN
Biopsy of a skin lesion can establish an RMSF diagnosis, although sensitivity of this test may decline after initiation of antibiotic therapy. Antibody reactivity to Rickettsia rickettsii antigen should be considered spotted fever group reactive. Because Rickettsia rickettsii is closely related to other Rickettsia species, assays may cross-react with other rickettsial species such as Rickettsia akari and Rickettsia parkeri. Measurement of IgM alone is not recommended. Serology is generally used for retrospective diagnosis and includes paired acute and convalescent specimens collected 2-4 weeks apart and compared to identify a fourfold titer increase in immunoglobulin G (IgG) concentration or seroconversion from IgM to IgG. The testing strategy should be based on the timing of testing relative to symptom onset.

Treatment should not be delayed for laboratory test results. Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) is a serious disease caused by Rickettsia rickettsii and should be treated immediately if suspected, due to its high mortality rate in the absence of appropriate medical intervention. If neurologic manifestations (eg, cranial neuropathy, meningitis, cranial nerve deficits, or encephalitis) are present, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) studies are necessary.ĭetailed information about laboratory testing for Lyme disease can be found in the Lyme Disease Testing Algorithm. For second-tier immunoblot testing, only immunoglobulin G (IgG) testing is necessary for specimens taken ≥4 weeks after disease onset, due to higher antibody concentrations. In 2019, the CDC introduced a modified two-tiered strategy that relies on two sequential or concurrent EIAs. Conventional two-tiered Lyme disease testing strategies include a first-tier enzyme immunoassay (EIA) followed by an immunoblot assay. When performing testing, the CDC’s two-tier testing strategy should be used. Additionally, in patients who exhibit a characteristic erythema migrans (EM) rash and have had exposure to an area in which Lyme disease is endemic, laboratory testing is not necessary for diagnosis. If Lyme disease is suspected, treatment should not be delayed for laboratory test results. However, although laboratory testing can confirm diagnosis and inform treatment, medical intervention should not be delayed in patients with a suggestive clinical presentation. The appropriate testing strategy depends on the suspected infection and duration of symptoms. Laboratory testing for tickborne disease includes serology and nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT). Laboratory testing may aid in determining the treatment that can best minimize the risk of severe illness when tickborne disease is suspected. Many tickborne illnesses have similar clinical presentations, including fever, headache, fatigue, and, in rare cases, paralysis (tick paralysis). Some of the more common tickborne diseases in the U.S. Tickborne diseases are transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected tick, and infections typically occur during the summer months when ticks are most active.
Tickborne diseases, including Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever, are increasing in incidence and distribution in the United States.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
